
Low-power Solenoid Coils significantly reduce electrical consumption in pneumatic systems. These coils minimize heat generation and extend component lifespan. This directly addresses high energy demands.
Energy savings of up to 80% thanks to dual-coil technology.
These Solenoid Coils offer substantial energy savings and operational benefits beyond just power reduction.
Key Takeaways
- Low-power solenoid coils save a lot of energy in pneumatic systems. They use less electricity than older coils.
- These coils make less heat. This helps parts last longer and makes the system more reliable.
- Using low-power coils helps the environment. They lower energy use and reduce carbon pollution.
The Energy Challenge in Pneumatic Systems

Understanding Pneumatic System Energy Consumption
Pneumatic systems face significant energy challenges. They often waste a lot of energy. Primary sources of energy loss include leaks, using too much pressure, and not regulating the return stroke. Machines left on when not in use also consume unnecessary power. Component sizing also plays a role. Using parts that are too small makes compressors work harder. Oversized components also lead to substantial energy losses. Leaks are a major problem. They often occur in seals and valves. The Department of Energy estimates that leaks waste 20-30% of a compressor’s output. Operators sometimes apply more pressure than needed, thinking it improves performance. This practice wastes energy.
The Energy Footprint of Traditional Solenoid Coils
Traditional components contribute to this energy footprint. The power consumption of a solenoid coil directly relates to its voltage and current. Engineers calculate this using the formula P = VI (Power = Voltage × Current). Minimizing power consumption is a key goal in applications where energy efficiency is critical. Some DC Solenoid Coils have special features to reduce power. These features include pulsed power supplies or dual-coil designs. These designs allow for a lower holding current after the initial activation. Evaluating the power consumption of these coils over their entire operating cycle helps ensure they meet application needs.
What Are Low-Power Solenoid Coils?
Definition and Core Technology of Low-Power Solenoid Coils
Low-power solenoid coils represent a significant advancement in pneumatic system components. Engineers design these coils specifically to minimize electrical energy consumption. They achieve this reduction without compromising performance. The core technology involves innovative materials and precise engineering. For instance, nano-structured magnetic cores allow for greater magnetic flux density in smaller spaces. This design creates compact solenoid magnets without sacrificing power output. Copper-clad aluminum windings also improve the reliability and efficiency of these advanced Solenoid Coils. High-temperature insulation coatings further enhance heat resistance. This allows for increased power density and reduces thermal degradation and energy loss.
Mechanisms for Reduced Power Consumption in Solenoid Coils
Several mechanisms contribute to the reduced power consumption of these coils. Smart materials and nanocomposites improve heat resistance, minimizing thermal degradation and energy loss. Beyond materials, driving strategies play a crucial role. Pulse-width modulation (PWM) is a driving strategy that cuts energy use in long-duty-cycle applications. Low-hold-current driving strategies also reduce energy consumption in applications with extended duty cycles. Manufacturers construct solenoid valves with tighter tolerances. This improves overall efficiency. Mechanical and magnetic optimizations further contribute to reduced power consumption. These design improvements lead to greater operational efficiencies across the entire system.
Direct Impact on Energy Efficiency with Low-Power Solenoid Coils
Quantifiable Electrical Savings
Low-power solenoid coils offer clear electrical savings. These savings are measurable and directly impact operational costs. For example, a customer in a remote natural gas wellhead application replaced 1.8-watt solenoid valves with ASCO’s 0.55-watt low-power versions. This change allowed them to use smaller solar panels and fewer batteries for the system. The energy savings also provided flexibility to add more controls later, improving overall application efficiency. Latching valves further reduce power consumption. They decrease the voltage needed to hold the plunger open by about 80% after initial activation. This significantly cuts down continuous power draw.
Reduced Heat Generation and Its Benefits
Low-power solenoid coils also generate much less heat. This reduction brings several benefits. Compared to standard coils, low-power versions show a significant decrease in wattage.
| Coil Type | Wattage | Reduction in Wattage |
|---|---|---|
| Standard XX | 9.5 watts | N/A |
| Upgraded XXN4 (low-power) | 1.8 watts | Over 80% |
| Traditional D-series direct-acting | 2.6 watts | N/A |
| D-series with low-power suppressor | 1.3 watts | 50% |
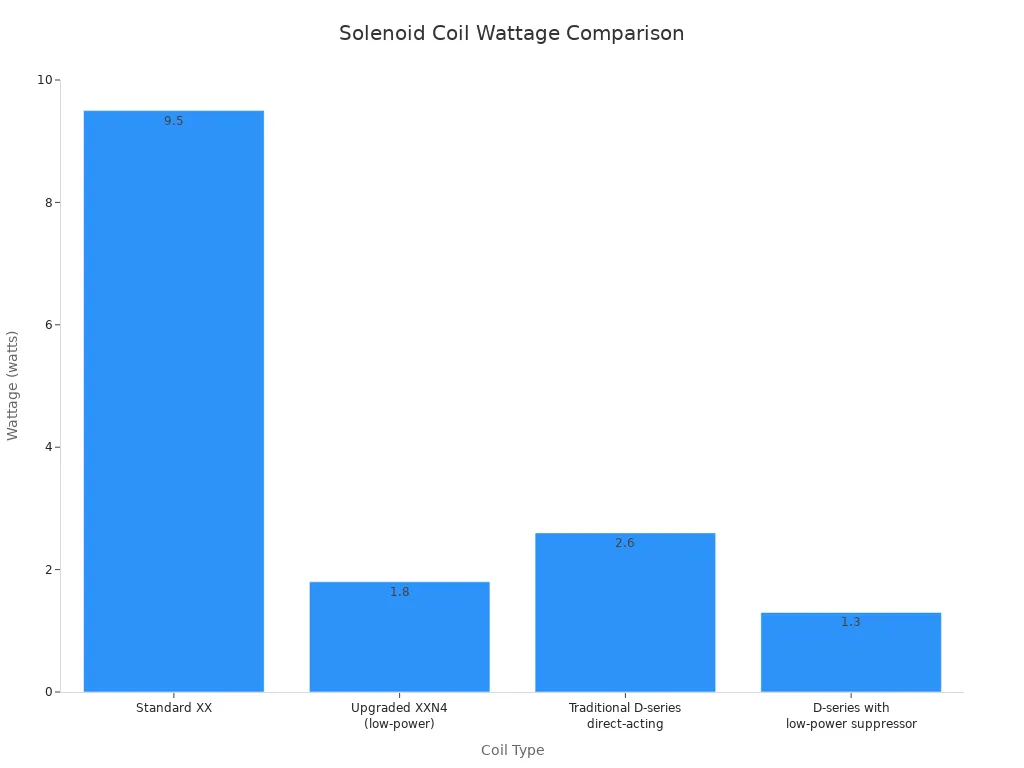
Low-watt coils can nearly double a valve’s maximum ambient temperature rating. This shows a substantial decrease in heat generation. Standard coils often limit a system’s ambient temperature ratings due to their higher heat output. Proper insulation helps reduce heat generation and loss. This offers significant advantages for system performance. It helps prevent temperature fluctuations. It also stops external factors from negatively impacting performance. This ensures the system operates consistently within its designed parameters. This also contributes to the system’s longevity and safety. Reduced heat generation, often helped by components like heat spreaders, offers specific benefits:
- Prevents Component Damage: Dissipating heat stops components from overheating. This extends their lifespan and boosts the device’s overall reliability.
- Improves Performance: Devices operate within their optimal thermal ranges. This prevents performance degradation caused by thermal throttling.
- Enhances Safety: It minimizes the risk of burns from hot surfaces. It also reduces the potential for fires by preventing overheating.
Contribution to Overall System Efficiency
Low-power solenoid coils significantly improve the overall energy efficiency of a pneumatic system. Solenoid valves primarily consume power only during their actuation period. This is especially true when configured with latching mechanisms. This characteristic reduces operating costs in applications where power control is critical. Examples include portable devices or energy-conscious manufacturing environments. They achieve this without compromising speed. Modern controllers further enhance efficiency. They monitor current draw and optimize timing. Recent advancements in solenoid coil technologies have greatly improved solenoid valve efficiency. Some sources indicate an 80% boost. These improvements lead to reduced energy consumption and faster response times. They enhance the overall efficiency of the system. Optimizing valve performance is crucial for energy-intensive systems like HVAC. Even small gains in component efficiency can lead to substantial overall system improvements. The design of a solenoid coil greatly impacts the energy efficiency of a 3/2 solenoid valve. Coils with low resistance need less electrical current to create the magnetic field for actuation. Coils with high magnetic efficiency convert electrical energy into magnetic energy better. This energy moves the valve’s internal components. Both low resistance and high magnetic efficiency improve energy efficiency. They reduce the power input needed for desired flow control.
Beyond Energy: Additional Benefits of Low-Power Solenoid Coils
Low-power Solenoid Coils offer advantages beyond simple energy savings. They significantly improve system longevity, reliability, and environmental performance. These benefits contribute to a more robust and sustainable operational environment.
Extended Component Lifespan
Low-power solenoid coils dramatically extend the lifespan of pneumatic system components. Traditional solenoids often experience burnout. This happens when a DC voltage equal to their AC rating is applied. The current then exceeds design specifications due to lower impedance in DC applications. Historically, manufacturers addressed this issue by applying a large current pulse for actuation. They then significantly reduced it to hold the solenoid. This mitigated thermal issues from prolonged power.
Traditional solenoids are also prone to failure from coil burnout. Excessive electrical current damages the coil windings. This prevents proper function. Overheating and noise can also occur. These issues result from incorrect voltage supply, internal resistance buildup, or mechanical friction. Operating a solenoid at a voltage higher than its rated capacity leads to overheating and potential coil burnout. Low-power consumption models, such as those using double coil technology or energy-saving coil designs, mitigate these issues. They reduce the power required to hold the valve in position after actuation. This prevents overheating and extends lifespan. Fewer heating cycles extend insulation life. They also delay coil replacement. This reduces unplanned downtime due to component failures. Reduced wear and tear from lower heat generation further extends valve lifespan.
Enhanced System Reliability and Stability
Low-power solenoid coils enhance overall system reliability and stability. Magnetic latching solenoids retain their last position during power failures. This prevents unintended actuation. It also supports consistent restart behavior. Modern low-power solenoid-operated valves (SOVs) consume as little as 0.55 watts. This significantly improves energy efficiency. Kick and Drop technology reduces power consumption by up to 80%. It uses a high initial current for activation and a reduced holding current. This reduced power consumption decreases wear and tear. It extends valve lifespan and ensures consistent performance. Durable designs require minimal maintenance. This directly decreases downtime and operational costs. Reduced energy consumption lowers operational costs. It also decreases HVAC load. This contributes to overall system reliability. Decreased field diagnostics and system recalibration due to coil fatigue reduce support labor hours. They also simplify maintenance.
High-frequency noise, such as coil whine, in electrical components signifies energy inefficiencies. This noise indicates electrical energy converts into acoustic energy. This represents a direct loss in the power conversion process. Such inefficiencies, though seemingly minor individually, lead to substantial energy waste in large-scale operations. Coil whine often links to rapid voltage fluctuations and high-frequency switching. These contribute to increased electromagnetic interference (EMI) and power quality issues. This potentially affects the performance and lifespan of sensitive electronic components. Addressing coil whine optimizes power delivery and consumption. It improves overall system stability and longevity. Electrical noise, defined as unwanted electrical signals, interferes with electronic circuits. This is particularly true in temperature controllers and control systems. Noise causes inaccurate readings, unstable performance, and even system failure. Minimizing electrical noise is crucial for maintaining safe, accurate, and efficient operations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Low-power solenoid coils play a crucial role in environmental sustainability efforts. There is an increasing demand for low-power solenoid valves. Companies seek to reduce their energy consumption and carbon footprint. Manufacturers respond by developing these valves. They significantly reduce energy consumption while maintaining high performance. This contributes to reduced operational costs and corporate sustainability goals. Adopting low-power solenoid coils, specifically through implementing low-power holding circuits or pulse-width modulation (PWM) control techniques, can lead to a reduction in energy consumption by up to 50% in some cases. This energy efficiency improvement directly translates to decreased greenhouse gas emissions. These emissions associate with power generation. This reduces the carbon footprint. Innovations such as low-power solenoid coils are becoming standard in manufacturing. They enable industries to reduce their carbon footprint and operational costs. This aligns with regulatory standards and corporate sustainability goals. While low-power solenoid coils contribute to safety and operational efficiency, which indirectly leads to environmental benefits like reduced energy consumption and emissions, they are not explicitly stated to help achieve specific environmental certifications or standards for the coils themselves. Certifications like UL, FM, ATEX, IECEx, CSA, CE, RoHS, and NSF primarily focus on safety, performance, and regulatory compliance.
Implementing Low-Power Solenoid Coils in Your System

Retrofitting vs. New Installations
Integrating low-power coils into pneumatic systems involves two main approaches: retrofitting existing setups or designing new installations. Retrofitting requires careful consideration of compatibility. Engineers must confirm the control voltage aligns with existing DC 12V/24V systems and signal protocols. They also ensure the coil mechanically fits existing mounting brackets or valve bodies. Standardized interfaces, like M3 or M4 threading, simplify this process. Wireless connectivity, using protocols such as Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) or LoRaWAN, can also facilitate remote monitoring for retrofitted valves.
For new installations, low-power coils offer significant advantages from the outset. They enhance energy efficiency, leading to reduced electricity bills. These coils also provide rapid response times, optimizing cycle rates in high-speed automation. Their rugged durability and longevity, designed for harsh industrial environments, contribute to a longer service life. This reduces downtime. New designs benefit from the versatility of these coils, allowing seamless integration into smart factories. This approach maximizes return on investment through lower operational costs and extended component life.
Key Considerations for Solenoid Coil Selection
Selecting the right low-power coil requires attention to several critical factors. Engineers must choose a voltage (12V, 24V, 110V, 220V AC/DC) that matches the system’s control logic. They also consider electrical features like low inrush current or power-saving coils for continuous operation. Voltage stability is crucial; fluctuations can cause overheating or incomplete valve actuation. Using regulated power supplies or surge protection helps maintain consistent electrical input.
Environmental ratings are also important. IP-rated enclosures prevent condensation and protect coils from moisture. Coil insulation class, such as Class F or H, ensures the coil withstands operating heat levels. Certifications like CE, RoHS, UL, and CSA confirm compliance with industry standards.
Calculating Potential Savings and ROI
Calculating potential savings and return on investment (ROI) for low-power coils involves assessing reduced energy consumption and extended component lifespan. Engineers quantify electrical savings by comparing the wattage of traditional coils to low-power alternatives. They also factor in decreased maintenance costs due to fewer coil replacements and reduced downtime. These calculations demonstrate the financial benefits of adopting low-power technology.
Low-power solenoid coils offer a critical, cost-effective solution for significant energy efficiency. They provide immediate financial returns through reduced electricity costs and long-term operational benefits like high reliability and extended service life. These coils also optimize energy consumption and minimize heat generation, significantly reducing environmental impact. Adopting these efficient coils represents a smart investment for sustainable pneumatic systems.
FAQ
What defines a low-power solenoid coil?
Low-power solenoid coils use innovative materials and precise engineering. They minimize electrical energy consumption without sacrificing performance.
How do low-power solenoid coils reduce heat?
They consume less wattage than standard coils. This significantly reduces heat generation. Less heat prevents component damage and improves performance.
What are the main benefits of using low-power coils?
They offer significant electrical savings and reduce heat. They also extend component lifespan, enhance system reliability, and improve environmental sustainability.
Post time: Dec-09-2025
