
Cartridge valve design fundamentally reduces equipment size and mass. Compact valve blocks are central to achieving significant space and weight reductions. This often results in 42% smaller machine footprints for mobile equipment. Integrated manifolds, a key aspect of hydraulic cartridge valve systems, also reduce external tubing by approximately 70%. This integration enhances equipment performance, reliability, and safety.
Key Takeaways
- Cartridge valves make machines smaller and lighter. They combine many parts into one unit. This saves a lot of space and reduces the machine’s weight.
- These valves make hydraulic systems work better and last longer. They have fewer parts that can leak. This means less downtime and safer operation.
- Cartridge valves are good for many uses. They help mobile machines, airplanes, and factory equipment. They make these machines more efficient and reliable.
The Evolution of Hydraulic Cartridge Valve Integration

Replacing Complex Assemblies with Integrated Solutions
Hydraulic systems traditionally relied on numerous discrete components, each performing a single function. These systems often involved complex arrangements of individual valves, fittings, and extensive piping. The advent of cartridge valve technology fundamentally changed this approach. Cartridge valves are standardized and modular hydraulic components. Manufacturers design them for insertion into specific valve block holes, where they cooperate with control cover plates. This inherent modularity allows them to perform various control functions. They integrate multiple functions into a single, compact unit. For example, a single cartridge unit, composed of a main valve and a control cover plate, achieves on-off, flow regulation, and logical control functions. These functions would typically require several separate components in a conventional system. Furthermore, cartridge valves incorporate pilot control valves, such as electromagnetic directional control valves or pressure valves. This capability enhances their flexibility, enabling more complex logical control over direction, pressure, and flow regulation within one integrated unit. This design significantly simplifies hydraulic circuits and reduces the overall component count.
Reducing Piping and Connection Points
Traditional hydraulic systems demand extensive external piping and numerous connection points. Each connection introduces a potential leak path and adds to the system’s complexity and weight. Cartridge valve integration directly addresses these challenges. Combining multiple valve functions into a single cartridge drastically reduces the need for external connections. For instance, a 2-way, 2-position SP proportional valve typically pairs with a pressure compensator. However, advanced designs integrate both the flow control and pressure compensator into the same cartridge, thereby reducing external connections. Manifolds, or ‘combination valves,’ further enhance this reduction. They consolidate numerous separate valve components and their connecting hoses and plumbing into internal drillings within a single block of aluminum. This eliminates dozens of hoses and fittings that would otherwise be necessary to connect individual valves. One customer, for example, used a single pressure reducing valve in a custom manifold with a gauge port and six work ports. This setup replaced a ‘mess of tees, junctions and connections,’ saving significant installation time and hose/fitting costs. This approach minimizes potential leak points and improves system reliability.
Streamlining Equipment Footprint
The integration of hydraulic cartridge valve technology directly contributes to a streamlined equipment footprint. By replacing complex assemblies with integrated solutions and significantly reducing piping and connection points, equipment designers achieve remarkable space savings. The compact nature of cartridge valves and their manifold integration allows for much smaller hydraulic power units and control blocks. This reduction in physical size is critical for mobile equipment, where space is at a premium. It also benefits industrial machinery and automation, where compact designs improve factory floor utilization. The elimination of external hoses and fittings not only saves space but also reduces clutter, making maintenance access easier and improving the overall aesthetic of the equipment. This streamlined footprint translates into more efficient machine designs, lower manufacturing costs, and enhanced operational flexibility.
Optimizing Performance and Reliability with Compact Valve Blocks

Embedded Flow Paths for Enhanced Efficiency
Compact valve blocks significantly enhance hydraulic system efficiency through their embedded flow paths. New cartridge valve designs focus on reducing energy consumption. For example, the LC8X logic cartridge valve minimizes pressure drops and optimizes variance. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations help engineers reduce pressure drops during the design phase. Valves designed with optimized internal flow paths minimize resistance. Manifold blocks integrate valves and flow paths, eliminating a maze of hoses and fittings. This integration streamlines fluid flow and reduces turbulence associated with numerous connections.
Valve blocks can lower energy consumption by 15 to 20 percent. Modern valve blocks use precision-milled internal channels. These channels replace up to 80% of external piping. Optimized geometry leads to 35% shorter fluid paths. This design also eliminates 22–28 flanged connections per circuit. It reduces potential leak points by 50%, meeting ISO 4413:2024 standards. The average pressure drop reduces from 28 bar in traditional piping to 9 bar in a valve block system.
Reduced Leakage Risks and Improved System Integrity
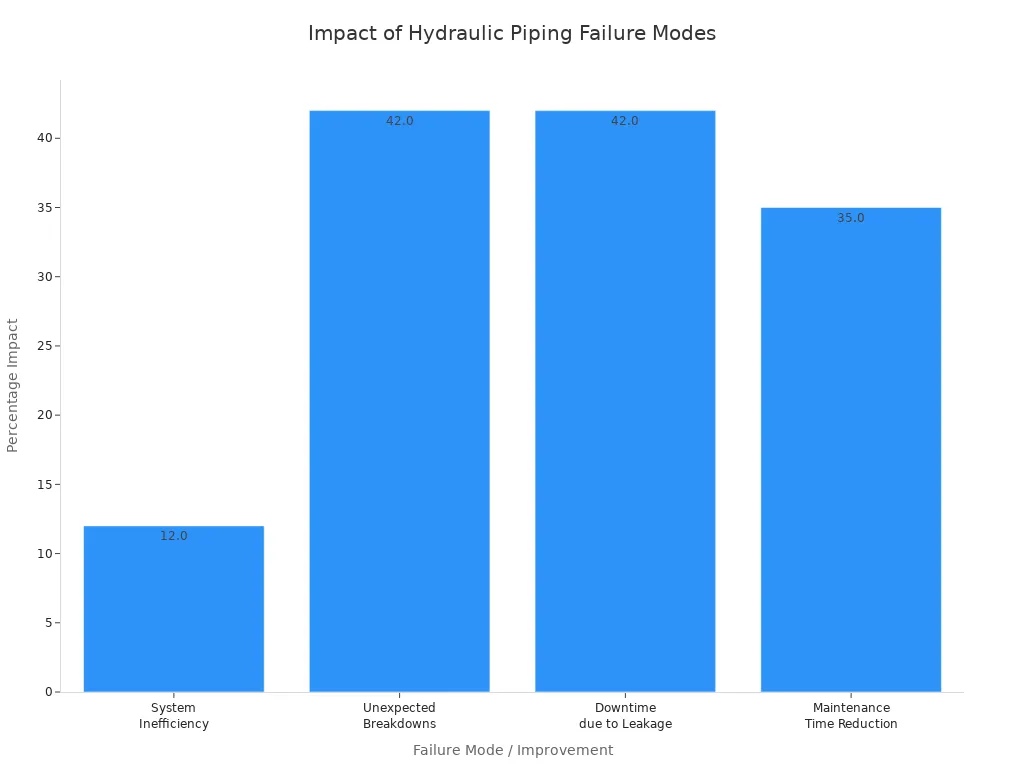
External hydraulic piping often suffers from common failure modes, primarily leakage and system inefficiency. Excessive piping reduces efficiency by 12-15%, according to a Fluid Power Efficiency Report from last year. Older pipe arrangements experience 42% more breakdowns compared to modern valve block technology, as studies on hydraulic cylinders show. Leakage is a major cause of downtime. It costs manufacturers approximately $740,000 annually in lost production time, according to Ponemon’s latest report (2023). Downtime due to leakage accounts for about 42% of all hydraulic cylinder downtime in heavy equipment, based on industry-wide observations.
| Failure Mode | Impact/Statistic | Source/Context |
|---|---|---|
| System Inefficiency (Excessive Piping) | Reduces efficiency by 12-15% | Fluid Power Efficiency Report (last year) |
| Unexpected Breakdowns (Older Pipe Arrangements) | 42% more breakdowns compared to modern valve block technology | Studies on hydraulic cylinders |
| Leakage (Major Cause of Downtime) | Costs manufacturers ~$740,000 annually in lost production time | Ponemon’s latest report (2023) |
| Downtime due to Leakage | Accounts for ~42% of all hydraulic cylinder downtime in heavy equipment | Industry-wide observations |
| Long-term Leakage Rates (Sealing Technology) | Monoblocks show zero external seepage after 10,000 pressure cycles, while stacked designs exhibit minor weepage, indicating a 5:1 difference in long-term leakage rates | Fluid power study |
| Maintenance Time Reduction (DBB Systems) | Technicians complete tasks ~35% quicker | Field reports from workshops |
Common failure modes associated with external hydraulic piping primarily revolve around leakage and system inefficiency. Excessive piping leads to significant pressure losses and heat buildup. This impacts equipment performance, especially in constantly cycling machinery like forging presses. Older systems, with numerous connection points (often around 30 per circuit), multiply the chances of failure. Leakage is a major cause of downtime. It creates hundreds of potential failure points due to standard piping setups with tube connections and flanged joints. These are vulnerable to vibrations and pressure changes. Once a leak occurs, dirt and debris can enter the system. This causes issues like sticky valve spools, scored cylinders, and accelerated wear.
Cartridge valve blocks mitigate these risks through integrated designs:
- Reduced Connection Points: Integrating multiple functions into a single block significantly reduces the number of external pipes, hoses, and fittings. This directly minimizes potential leak paths.
- Shortened Fluid Paths: Compact designs lead to shorter internal fluid galleries. This reduces pressure losses, turbulence, and heat generation, thereby improving system efficiency.
- Monoblock Construction: Single-piece manifolds eliminate gaskets. They use precision-machined internal galleries. This removes interfaces prone to thermal cycling and extrusion, common causes of leaks.
- Gasket-Sealed Modular Designs: While still using seals, these designs require strict bolt torque control. This prevents creep-induced leaks, offering a serviceable alternative.
Double-Block-and-Bleed (DBB) Integration for Enhanced Safety
Double-Block-and-Bleed (DBB) integration in compact valve blocks significantly enhances safety. DBB valve blocks are compact manifolds. They combine two isolation valves and a central bleed port. This design allows safe pressure release between seals before maintenance. It prevents unexpected fluid spills. They also include strategically located test ports for immediate pressure checks. This ensures a zero-energy state before servicing. Field reports from workshops indicate technicians complete tasks approximately 35% quicker with DBB systems.
Several safety standards and regulations address the integration of DBB functionality:
- NORSOK P-001: This standard recognizes and mandates the use of DBB valves for isolation.
- OSHA: The Occupational Safety and Health Administration recognizes Double Block & Bleed systems as a means of isolation. This is similar to physical separation. It helps remove a permit space from service and protects against energy and material release.
Other standards also provide guidance:
- API 6D: This standard specifies DBB applications for pipeline systems. It defines DBB as a single valve with two seating surfaces. When closed, it seals against pressure from both ends. It also has a means to vent or bleed the cavity between surfaces.
- ASME B31.3: This provides guidance for process piping applications, which often involve DBB.
- Internal Safety Standards: Many operating companies have established internal safety standards. These mandate DBB valves for specific service conditions. These conditions include high-pressure systems, hazardous fluid categories, and critical isolation points. A single valve failure in these areas could have severe consequences.
- OSHA 1910.146: This provides general safety principles and procedural steps for applying DBB across various industries. It describes closing and locking/tagging two inline valves and opening/locking/tagging a drain/vent valve between them.
- PHMSA (49 CFR Part 195 & 49 CFR Part 192): This implies or references DBB in regulations concerning pipeline integrity, maintenance, and emergency shutdown procedures. It addresses requirements for isolating pipelines containing hazardous liquids, often necessitating DBB.
The integration of DBB functionality within a Hydraulic Cartridge Valve system provides a robust safety solution.
Real-World Impact of Cartridge Valve Design
Case Studies in Mobile Hydraulics
Cartridge valve integration significantly benefits mobile hydraulic equipment. Excavators and agricultural machinery use these valves to control complex functions. These functions include boom articulation and implement movement. The compact size of cartridge valves allows integration into tight spaces. This reduces the overall machine footprint. The trend towards smaller, more powerful cartridge valves delivers more hydraulic power from a smaller physical footprint. This advancement leads to more compact machine designs. It also frees up valuable space in complex hydraulic manifolds. Smaller, more efficient valves contribute to lighter equipment and reduced material usage.
Aerospace and Defense Applications
Slip-in cartridge valves are increasingly in demand within the aerospace sector. Their lightweight construction and high performance are crucial. These valves offer an optimal solution where weight and efficiency are paramount. They support the industry’s drive for reduced fuel consumption and emissions. Advanced fluid control systems boost overall aircraft efficiency. Aluminum is widely used for these valves due to its light weight and corrosion resistance. Specialized alloys and composites also provide enhanced strength-to-weight ratios. These materials offer superior corrosion resistance, crucial for aerospace applications.
Oilgear designs custom hydraulic equipment with careful consideration for size and weight. This ensures operational safety, reliability, and performance. Their design process plans for space constraints, mounting positions, and port connections. They integrate cutting-edge technologies like ‘Hard-on-Hard’ technology and hydrodynamic bearings. These allow pumps and valves to perform in extreme temperatures and with specialized fluids. This meets the stringent requirements of aerospace and defense applications. HYPERFORMANCE™ High Pressure Valves are designed for high duty cycle, high horsepower, and high-pressure machine applications. They feature a 350 bar continuous operating pressure. They are fatigue tested to 420 bar, indicating enhanced system robustness. This robust design increases reliability and reduces contamination in demanding applications. Hydraulic Cartridge Valve technology provides compact designs, saving space in hydraulic systems. Their modular construction allows easy replacement and customization, contributing to system robustness.
Industrial Machinery and Automation
Cartridge valve systems offer significant advantages in industrial machinery. They provide straightforward installation and replacement due to their threaded design. This reduces downtime during servicing. Quality materials ensure high durability and longevity. This minimizes the frequency of replacements and repairs. The use of cartridge valves enhances productivity by reducing downtime and simplifying maintenance routines.
These systems integrate multiple functions into compact assemblies. This minimizes leak points and reduces system complexity. It also enhances reliability. Modularity enables rapid reconfiguration and easier maintenance. This leads to reduced downtime and lifecycle costs. Embedded sensors provide real-time data for predictive maintenance and dynamic optimization. This minimizes unplanned downtime. Integration with Industry 4.0 platforms facilitates remote diagnostics and seamless updates. This reduces human intervention. Cartridge valves are critical components in modern hydraulic systems. They offer precise control of fluid flow and pressure. Their compact, modular design allows easy integration and replacement within manifold blocks. This makes them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications.
Cartridge valve design delivers unparalleled space and weight savings. Compact valve blocks directly enhance equipment performance, reliability, and safety. These integrated solutions offer significant advantages. The future of equipment design increasingly relies on advanced Hydraulic Cartridge Valve technology. This ensures more efficient and robust systems.
FAQ
What is a cartridge valve?
Cartridge valves are modular hydraulic components. They insert into valve blocks. They perform various control functions. This design simplifies hydraulic circuits.
How do cartridge valves save space in equipment?
They integrate multiple functions into single units. This eliminates extensive piping and connections. This design allows for smaller hydraulic power units and control blocks.
What are the primary benefits of using cartridge valve systems?
They offer space and weight savings. They enhance performance and reliability. They also improve safety through integrated designs. This leads to more efficient equipment.
Post time: Dec-25-2025
