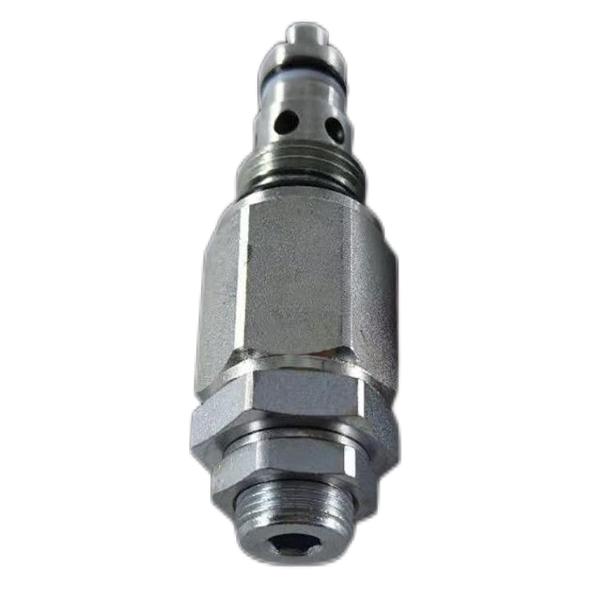
279834 Gas Valve Dryer Ignition Kit Solenoid Coil 24V
Details
Sealing material:279834 Gas Valve Dryer Ignition Kit Solenoid Coil 24V
Pressure environment:ordinary pressure
Temperature environment:one
Optional accessories: Solenoid Valve
Type of drive:power-driven
Applicable medium:petroleum products
Points for attention
An electromagnetic coil is an electronic component that works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. Its core structure is a spiral winding formed by a wire (usually a copper wire) wound on an iron core or other magnetic core material. When current passes through the wire, the coil generates a magnetic field; conversely, when the coil is in a changing magnetic field, it will also induce current. This characteristic makes it play a key role in many electrical devices.
Basic composition of electromagnetic coils
Winding
It is made of tightly wound insulated wires (such as enameled wires). The material, thickness, number of turns and winding method (such as single-layer winding, multi-layer winding, honeycomb winding, etc.) of the wire will directly affect the performance of the coil (such as inductance, resistance, rated current, etc.).
Magnetic core
Most coils are equipped with magnetic cores to enhance the magnetic field strength. Common magnetic core materials include:
Soft magnetic materials (such as silicon steel sheets, ferrites, and permalloys): suitable for alternating current scenarios (such as transformers and motors), which can reduce hysteresis losses;
Non-magnetic materials (such as plastics and air): used in high-frequency circuits (such as radio frequency coils) to avoid energy loss caused by magnetic cores.
Working principle: Electromagnetism and magnetism
Electromagnetism (magnetic field of current-carrying coil)
According to Oersted's experiment and Ampere's law, when current passes through a coil, a circular magnetic field will be generated around it. The direction of the magnetic field can be determined by the "right-hand screw rule": hold the coil with your right hand, with four fingers pointing in the direction of the current, and the thumb pointing to the N pole of the magnetic field. The magnetic field strength of the coil is proportional to the current size and the number of turns. If a magnetic core is added, the magnetic field will be significantly enhanced (the magnetic permeability of the magnetic core is much higher than that of air).
Electromagnetism (electromagnetic induction)
When the magnetic field in which the coil is located changes (such as the movement of a magnet, the change of current in other coils), according to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, an induced electromotive force (voltage) will be generated at both ends of the coil, and an induced current will be formed if the circuit is closed. This principle is the core working mechanism of equipment such as transformers, generators, and inductance sensors.
Product specification



Company details








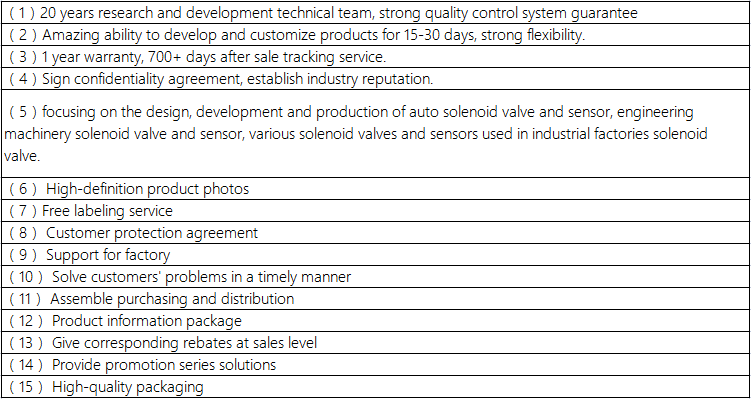
Company advantage
Transportation

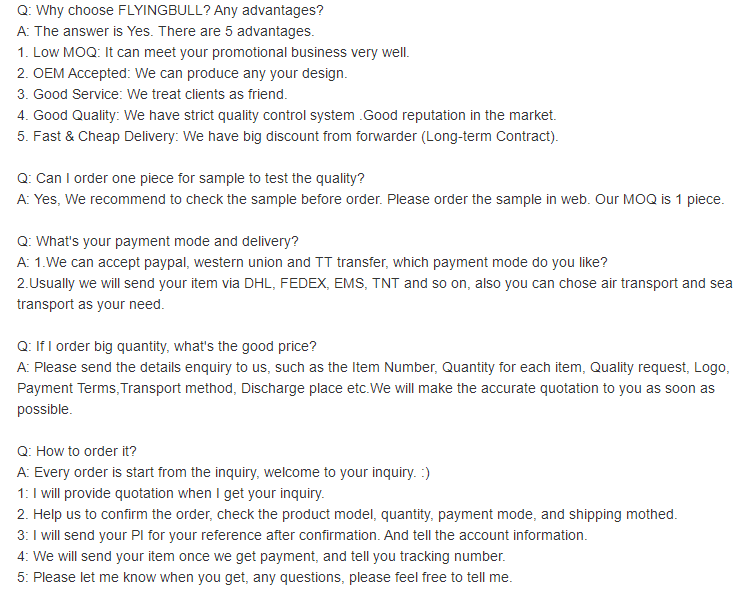
FAQ