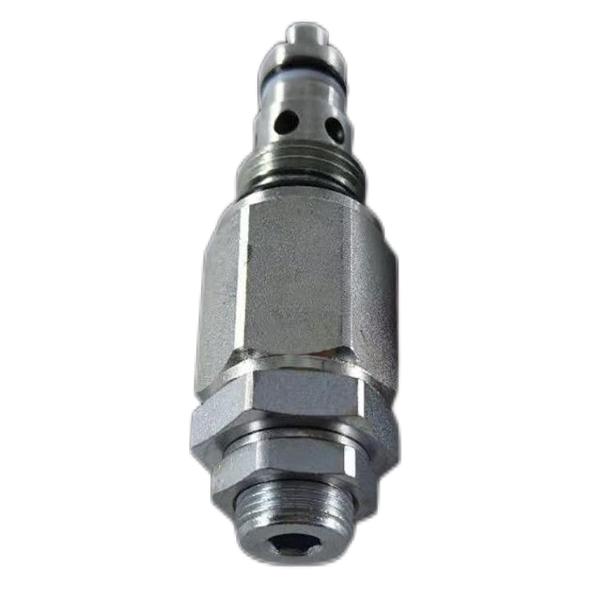
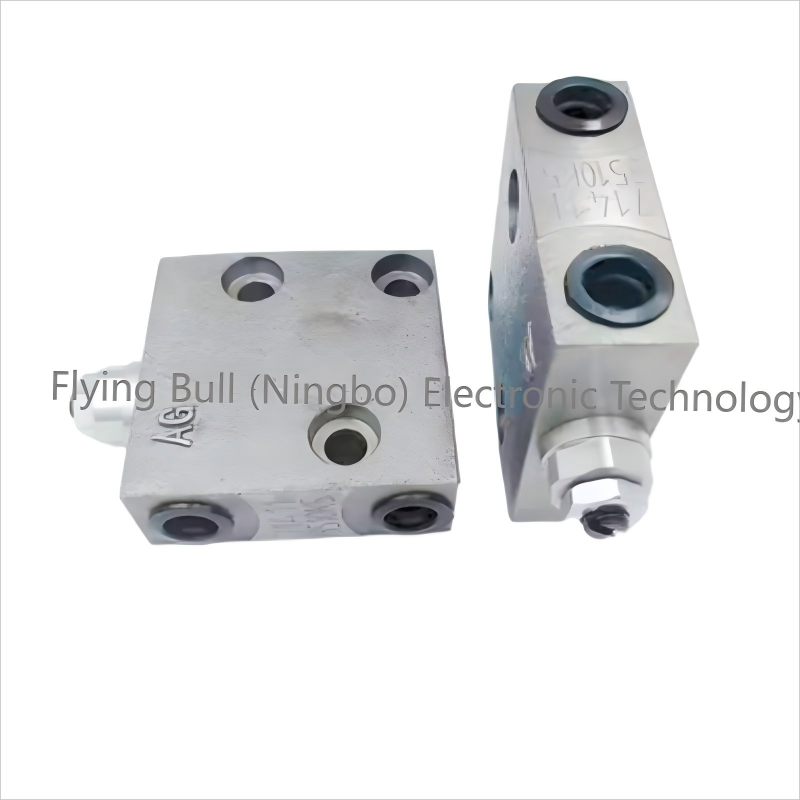
Pilot Valve 723-40-71900 PC200 PC220 PC228 PC240 PC270 PC290
Details
Sealing material:Pilot Valve
Pressure environment:ordinary pressure
Temperature environment:one
Optional accessories:Pilot Valve
Type of drive:power-driven
Applicable medium:petroleum products
Points for attention
A pilot valve is an auxiliary valve that plays a role in controlling the operation of the main valve in hydraulic, pneumatic or other fluid control systems. It is usually used in conjunction with the main valve and regulates the working state of the main valve by controlling the opening or closing of the pilot valve, thereby achieving control over the pressure, flow rate or direction of the fluid in the system. Working principle
The pilot valve itself is usually a relatively small valve, and its working principle is based on the pressure control principle in fluid mechanics:
Control the operation of the main valve: When the pilot valve opens, it releases or introduces a small portion of the control fluid (such as hydraulic oil, compressed air, etc.), thereby changing the pressure difference between the two ends of the main valve and causing it to open or close.
Signal transmission: The opening and closing of the pilot valve is controlled by external signals (such as electromagnetic force, mechanical force, pressure signals, etc.), and then the operation of the main valve is indirectly controlled to achieve the automatic control of the entire system.
Common types and application scenarios
According to the differences in structure and function, pilot valves can be classified into various types and are suitable for different systems:
Electromagnetic pilot valve
Structure: It is composed of an electromagnetic coil, an armature, a valve core, etc. The movement of the valve core is controlled by the magnetic force generated when the electromagnetic coil is energized or de-energized, thereby opening or closing the pilot valve.
Application: It is commonly used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems as a pilot valve for electromagnetic directional control valves, controlling the reversing of the main valve to achieve the control of the movement direction of actuating elements (such as hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders).
Pressure pilot valve
Structure: It uses fluid pressure as the control signal. When the system pressure reaches the set value, the pressure pushes the valve core to open or close the pilot valve.
Application: In pressure control valves such as pressure reducing valves and relief valves, it is used as a pilot valve to sense the system pressure and control the operation of the main valve to maintain the stability of the system pressure or limit the maximum pressure.
Mechanical pilot valve
Structure: The opening and closing of the pilot valve is controlled by the movement of mechanical components such as cams, levers, springs, etc.
Application: It is commonly found in some systems that require mechanical interlocking control, such as the hydraulic systems of certain machine tools, where the main valve's operation is controlled according to a predetermined program through a mechanical pilot valve.
Characteristics and Advantages
Precise control: Due to the small size of the pilot valve, the required control force is also relatively small. Therefore, precise control of the main valve can be achieved, thereby meeting the high-precision requirements of the system for parameters such as pressure and flow.
Flexible adjustment: By changing the set parameters of the pilot valve (such as the pressure set value, the energizing time of the electromagnetic coil, etc.), the working state of the main valve can be conveniently adjusted to adapt to different working conditions.
Safety protection: In some systems, pilot valves can also play a role in safety protection. For instance, when the system pressure exceeds the set value, the pressure pilot valve opens, causing the main valve to act, thereby releasing the pressure and preventing the system from being damaged due to excessive pressure.
The fit relationship with the main valve
The coordination between the pilot valve and the main valve forms a complete control system. The relationship between the two is as follows:
The pilot valve is the executor of control signals: it receives external control signals (such as electrical signals, pressure signals, etc.) and converts them into the flow or stop of the fluid, thereby controlling the operation of the main valve.
The main valve is the main body of fluid control: under the control of the pilot valve, the main valve opens or closes to achieve the on-off, pressure regulation or flow direction change of a large amount of fluid in the system.
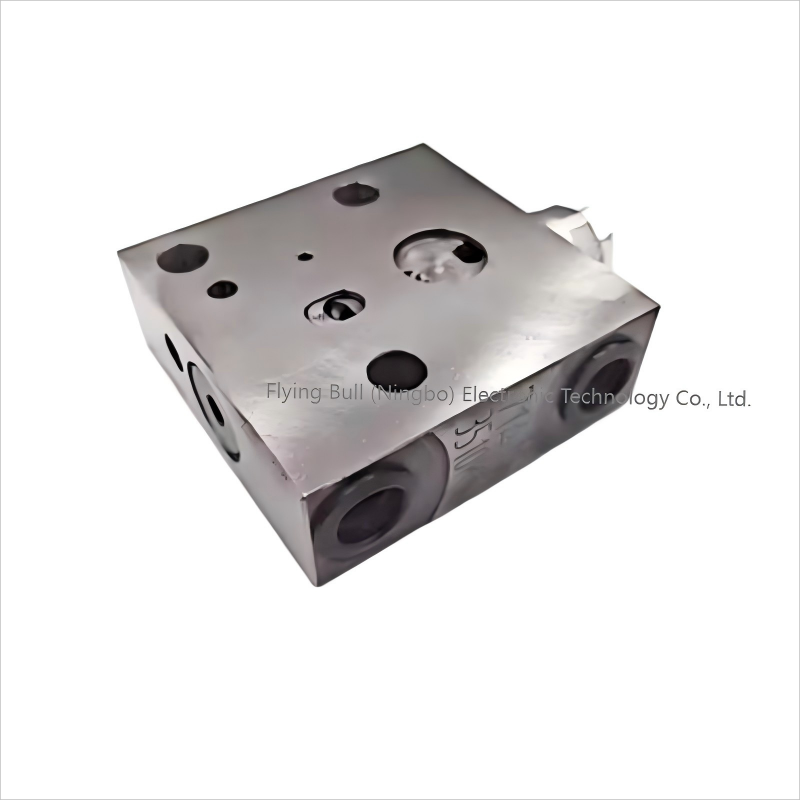
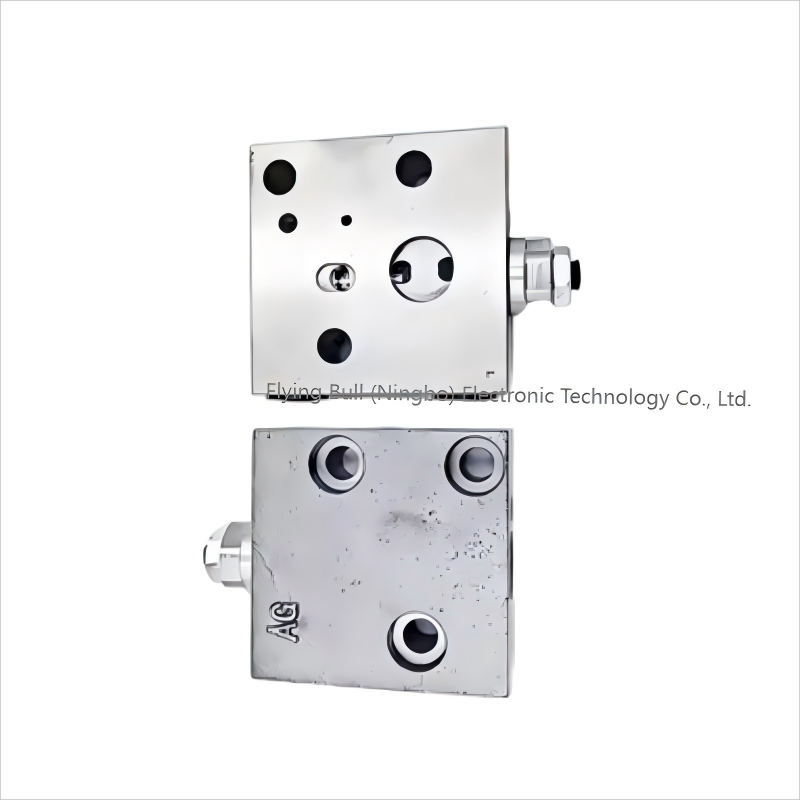
Product specification



Company details








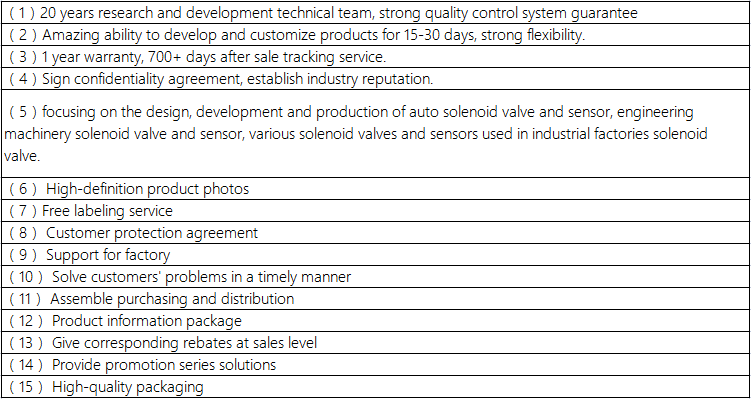
Company advantage
Transportation

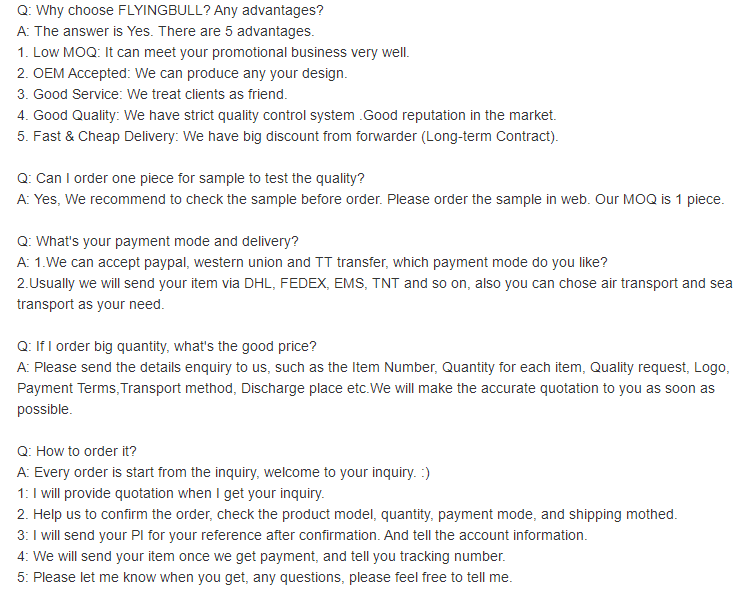
FAQ