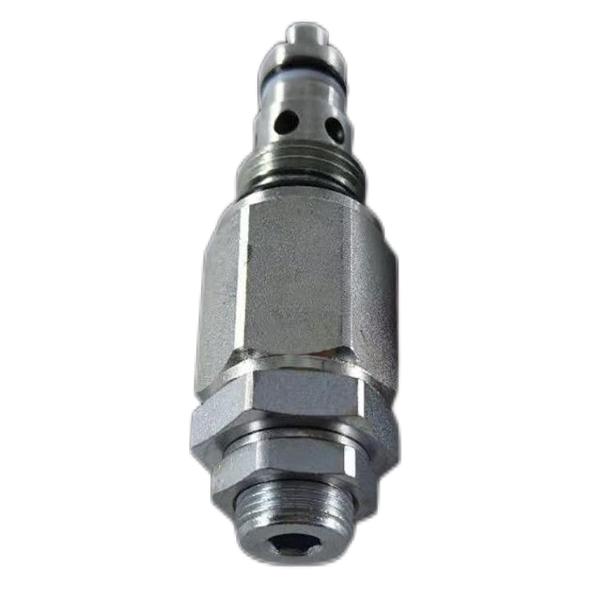
Solenoid Valve 3E8622
Details
Sealing material:Solenoid Valve 3E8622
Pressure environment:ordinary pressure
Temperature environment:one
Optional accessories: Solenoid Valve
Type of drive:power-driven
Applicable medium:petroleum products
Points for attention
An electromagnetic valve is an automated component that controls the on-off or flow direction of fluids through electromagnetic force. It is widely used in hydraulic, pneumatic, water supply and drainage systems, and is a key actuating component in the field of industrial automation
I. Basic Definitions and Core Functions
Definition: A valve that uses the magnetic force generated by the energizing of an electromagnetic coil to drive the valve core to act, thereby controlling the flow, cut-off or reversing of fluids (liquids, gases), belongs to the "electricity-magnetic-mechanical" conversion device.
Core functions:
Switch control: When powered on, the valve core operates to open the passage; when power is off, it is closed by spring return (such as a two-position two-way valve controlling the on-off of the oil passage).
Direction switching: Change the fluid flow direction through the displacement of the valve core (such as controlling the expansion and contraction direction of the oil cylinder with a three-position four-way valve);
Signal amplification: Control high-pressure fluids (such as 31.5MPa hydraulic systems) with weak current signals (such as DC 24V).
Ii. Working Principle and Typical Structure
1. Working principle and process
Electromagnetic drive stage: The electromagnetic coil is energized → a magnetic field is generated → the armature is attracted to drive the valve core to overcome the spring force and move.
Fluid control stage: The displacement of the valve core changes the on-off state of the valve port or the flow path → the fluid flows in the predetermined direction.
Reset stage: Power-off → Magnetic field disappears → Spring force pushes the valve core to reset → Fluid is cut off or returns to the initial state.
2. Structural Composition (Taking the two-position three-way solenoid valve as an example
Electromagnetic part
Electromagnetic coil (wound with enameled wire, voltage specification AC 220V/DC 24V, etc.)
Armature (soft magnetic material, such as silicon steel sheet), core (magnetic conduction circuit);
Magnetic isolation sleeve (copper or stainless steel, to prevent magnetic short circuits).
Mechanical part:
Valve core (cylindrical slide valve or ball valve, made of stainless steel/brass);
Spring (source of reset force, elastic coefficient designed according to pressure);
Valve body (aluminum alloy/cast iron, internally machined flow channel, interface thread such as G1/2).
Sealing part:
Sealing ring (nitrile rubber/fluorine rubber to prevent fluid leakage);
Sealing seat (hard alloy, resistant to high-pressure wear).
Product specification



Company details








Company advantage
Transportation

FAQ